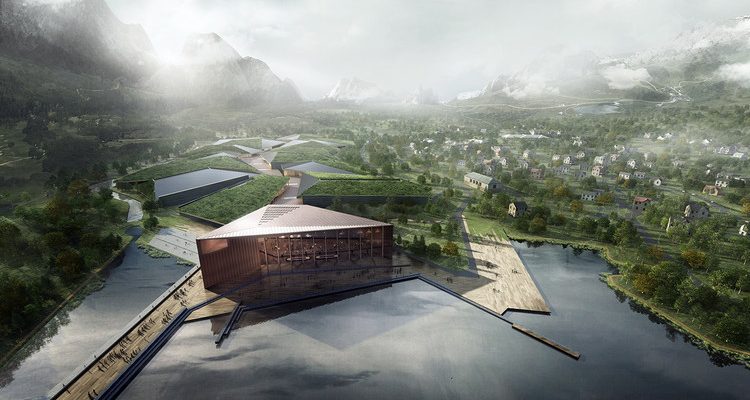
Data centers are the backbone of modern digital infrastructure, housing critical data and applications essential for business operations. Ensuring the security of these facilities is paramount to protect sensitive information and maintain operational integrity. Stendel + Reich data center architecture exemplifies the integration of robust security measures in modern data center designs.
Understanding Data Center Security
Security in data center architecture involves implementing comprehensive strategies to safeguard against physical and cyber threats. These strategies encompass a variety of measures, from physical security controls to advanced cybersecurity protocols.
Physical Security
Physical security is the first line of defense in a data center. It includes the design and implementation of barriers, surveillance systems, and access controls to prevent unauthorized entry. Effective physical security measures include:
- Perimeter Security: High fences, security gates, and surveillance cameras monitor the perimeter, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access the facility.
- Access Controls: Biometric scanners, keycards, and security personnel manage entry points, verifying the identity of individuals entering sensitive areas.
- Surveillance Systems: Continuous monitoring through CCTV and alarm systems detects and records any suspicious activities.
Cybersecurity Measures
In addition to physical security, robust cybersecurity measures are crucial. These include:
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Protect the network from unauthorized access and cyber-attacks.
- Encryption: Ensures that data remains secure during transmission and storage, preventing unauthorized access or tampering.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting frequent security audits helps identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
The Role of Architecture in Data Center Security
Architectural design plays a significant role in enhancing the security of data centers. Stendel + Reich data center architecture, for example, integrates security into the core design, creating a fortified environment that supports both physical and cybersecurity measures.
Design Considerations
- Zoning and Compartmentalization: Dividing the data center into secure zones limits access to critical areas, reducing the risk of internal threats.
- Redundancy and Resilience: Implementing redundant systems and backup power supplies ensures continuous operation, even during a security breach or power failure.
- Environmental Controls: Advanced HVAC systems and fire suppression technologies protect equipment from environmental hazards.
Best Practices
Adopting best practices in data center architecture is essential for maintaining security. This includes:
- Scalable Designs: Allowing for future expansions without compromising security.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulations, such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly updating security measures to address emerging threats.
Conclusion
Incorporating robust security measures into data center architecture is vital for protecting sensitive data and ensuring operational continuity. The example set by Stendel + Reich data center architecture demonstrates how integrating security into the design process can create a resilient and secure data center environment. By prioritizing both physical and cybersecurity, organizations can safeguard their critical infrastructure against a wide range of threats.









Comments